Energy trilemma evolving to reflect new ambitions and threats
Smart Energy International
APRIL 18, 2024
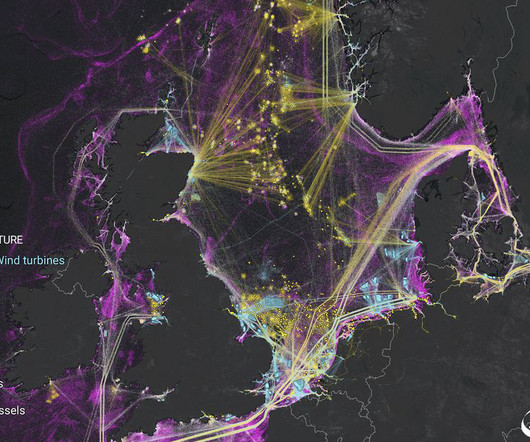
The World Energy Council’s World Energy Trilemma 2024 report reveals changing ambitions and new challenges facing global energy systems. Energy security now encompasses the reliability of renewables, availability and accessibility or critical minerals, and resilience in the face of physical and cyber threats.











Let's personalize your content