Highlights from the 2022 BP Statistical Review
R-Squared Energy
JULY 13, 2022
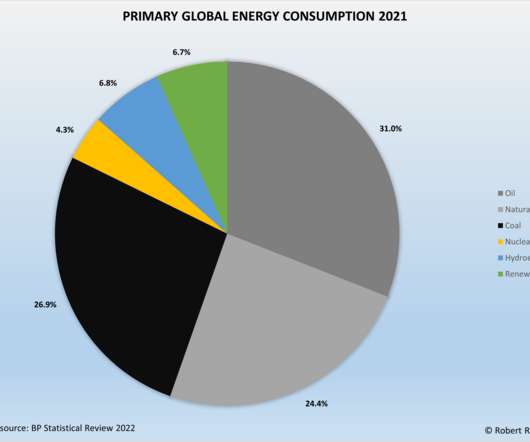
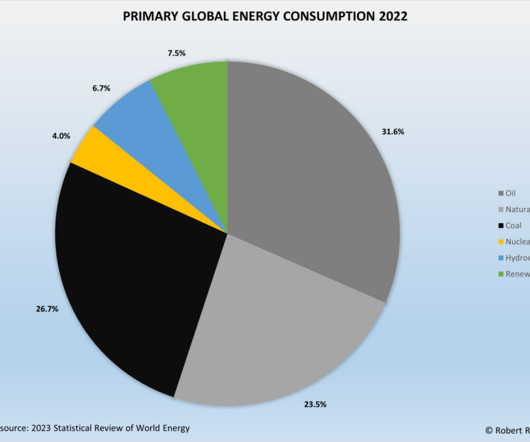
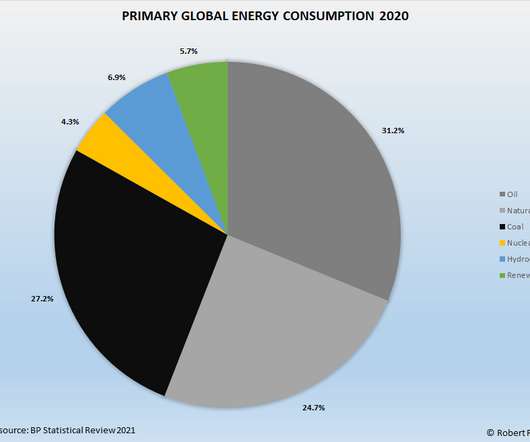
The remaining share of primary energy use consisted of hydroelectric power (6.8%), renewables (6.7%), and nuclear power (4.3%). Global carbon dioxide emissions rebounded from 2020 levels, growing by 5.9% Global coal consumption has been on a downward trend since peaking in 2014. Renewables and Nuclear Power.











Let's personalize your content