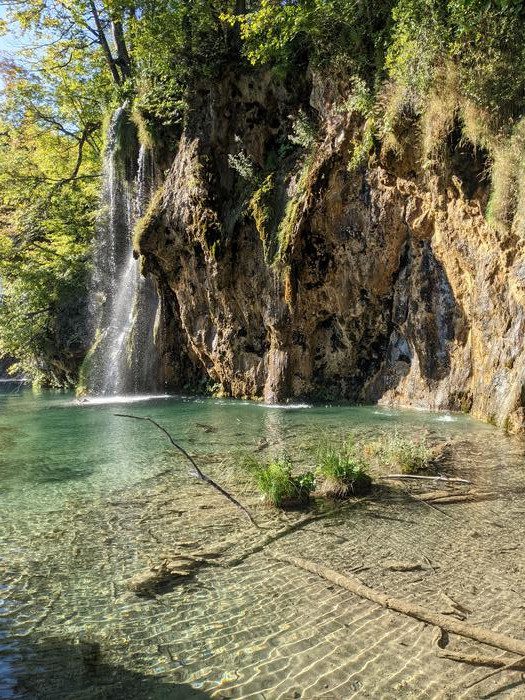
An international study classifies groundwater as a keystone ecosystem and proposes ways to improve its protection to preserve biodiversity and mitigate climate change
Water is the basis of all life on Earth. However, the crucial role of groundwater in sustaining both humanity and biodiversity over the long term is frequently neglected. In a recently published paper, an international team of researchers has outlined, for the first time, why groundwater should be treated as a keystone ecosystem. “Groundwater is not only in itself a major ecosystem but is also of critical relevance to ecosystems on the Earth’s surface,” emphasized Professor Robert Reinecke of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), a specialist in Earth system modeling. He made major contributions to the paper, which outlines concepts for improved groundwater protection to reduce the loss of biodiversity and to compensate for the effects of climate change.
Urban populations depend on it
Groundwater is the largest unfrozen reserve of freshwater on Earth. It supplies the drinking water needs of almost 50 percent of the world’s urban population. Countries such as Denmark, for example, obtain their drinking water entirely from groundwater. “Throughout the world, some 1,000 cubic kilometers of water are pumped to the Earth’s surface every year. Sadly, we consume far more than what is naturally replenished,” said Reinecke. About a third of the largest groundwater catchment areas are at risk of depletion, indicating an ongoing decline in groundwater levels.
The supply of drinking water for humans clearly is one aspect of the problem. Another aspect is the dependence of ecosystems on groundwater, which has been repeatedly overlooked in global biodiversity conservation agendas so far. Roughly 52 percent and thus more than half of all surface areas have a medium-to-high interaction with groundwater. This figure increases to 75 percent when excluding deserts and high mountains, regions where groundwater is scarce or the water table can be very deep. “Interaction in this context means that water from rivers and lakes enters the groundwater while groundwater, in its turn, rises to the surface and feeds wetlands, rivers, and other kinds of surface water areas.” Reinecke adds that groundwater is also a valuable habitat for thousands of different subterranean creatures, including cavefish, blind eels, and transparent shrimp.
Researchers propose a groundwater conservation agenda
As the researchers stated in their report published in Global Change Biology: “Disregarding the importance of groundwater as an ecosystem ignores its critical role in preserving surface biomes. To foster timely global conservation of groundwater, we propose elevating the concept of keystone species into the realm of ecosystems, claiming groundwater as a keystone ecosystem that influences the integrity of many dependent ecosystems.” 51 researchers from various countries – from Australia to India and the Philippines, from Italy and Finland to Brazil and Canada – participated in the study.
With regard to German law, Robert Reinecke points out that groundwater is not yet defined as a habitat under the German Federal Nature Conservation Act but only as a resource and is thus not subject to the corresponding protection. “We need to change this very urgently,” emphasized Reinecke, citing the statistics collected by the German Environment Agency (UBA) that show that the quality of approximately 32 percent of all groundwater bodies in Germany is poor because of chemical contamination. The main causes of this are nitrate levels and pollution by pesticides.
The researchers propose eight key themes to design a science-policy integrated groundwater conservation agenda. As given ecosystems above and below the ground intersect at many levels, it is essential to consider groundwater as a vital element determining the health of our planet – to mitigate the loss of biodiversity and provide a counterbalance to climate change. “Water is indispensable to life on Earth. If we don’t pay sufficient attention to the ecological integrity of the freshwater resources of our planet, we not only put the sustainability of whole ecosystems at risk but we also jeopardize our own way of life,” concluded Reinecke.